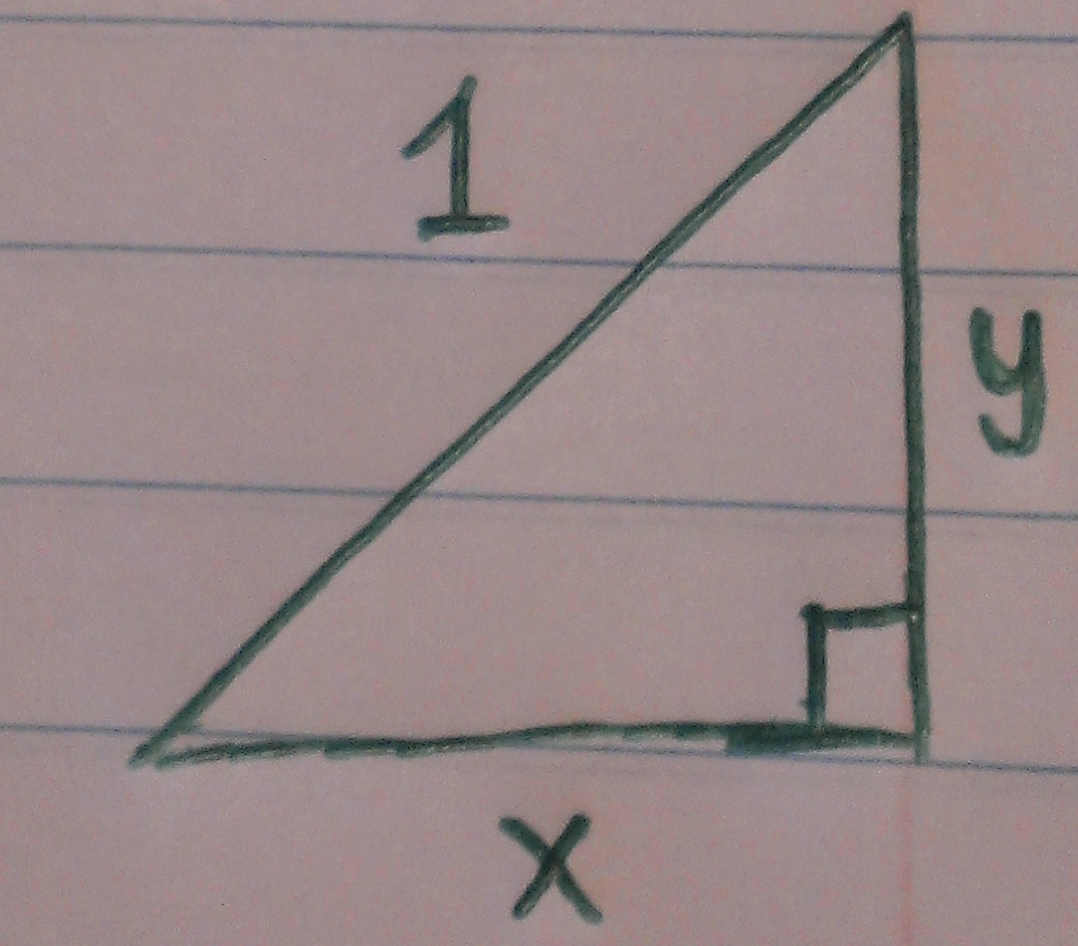Back to the class
Find the base and the height of a right triangle with hypotenuse $1$ whose perimeter is $11$ and whose area is a maximum.
Solution: Let $x$ and $y$ denote the legs of such a triangle and draw it:
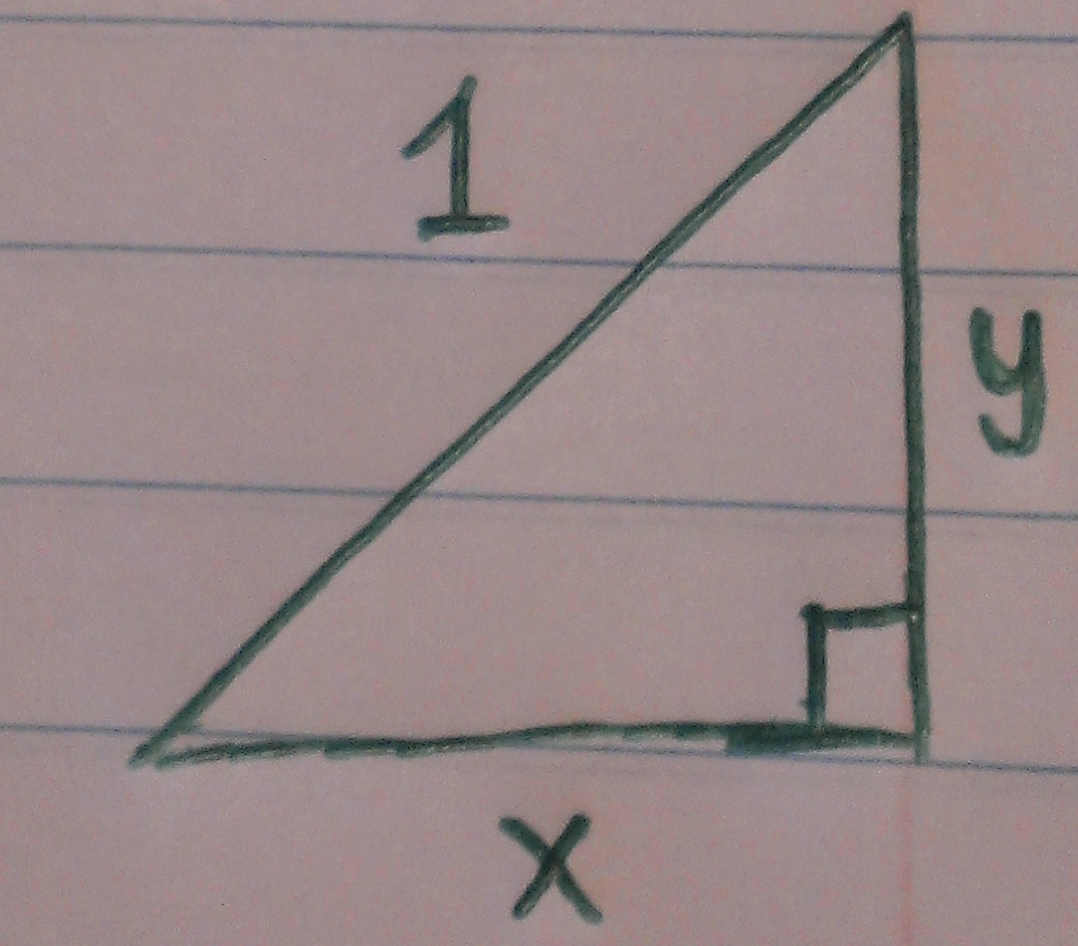
The perimeter of this triangle equalling $11$ is the constraint and can be written as
$$x+y+1=11.$$
We wish to optimize the area of this triangle
$$A=\dfrac{1}{2}xy.$$
Using the constraint, we can write $x=10-y$. Plugging this into the area formula yields
$$A = \dfrac{1}{2}(10-y)y=5y-\dfrac{y^2}{2}.$$
To optimize $A$, we will find the critical points and use the second derivative test. First compute
$$A'=5-y \stackrel{\rm{set}}{=} 0.$$
Therefore we get $5=y$. We must show that this is a maximum. To do so, compute
$$A''=-1.$$
Therefore we plug in our critical point and get
$$A''(5) = -1 < 0.$$
From the second derivative test, we may conclude that the area is a maximum when $y=5$. Using the constraint equation, we may conclude that $x=10-5=5$.